Summary
Karim Ghoufiri
Business developper
Technology
- Increasing evidence confirms that the gut microbiota is involved in a number of diseases, particularly in the development of obesity and related disorders.
- Turicimonas muris (T. muris) is a proteobacterium derived from the human gut microbiota.
- A negative correlation has been observed between the abundance of T. muris in the body and body weight.
- Using T. muris as a probiotic could help improve and prevent metabolic disturbances and weight gain in individuals with obesity.
- It may be administered alone or in combination with other bacteria or drugs intended for treatment.
- Additionally, T. muris could be used as an adjuvant in diabetes therapies or as a complement to bariatric surgery.
Market
- Today, nearly 50% of the European population and 17% of the French population are overweight or obese.
- However, available drug treatments for obesity remain limited and are mostly reserved for severe cases, despite the substantial costs associated with managing affected individuals.
- To prevent these conditions, control their progression, and reduce the significant costs of treatment, it is essential to develop non-invasive, more effective, and more affordable solutions.
Development status
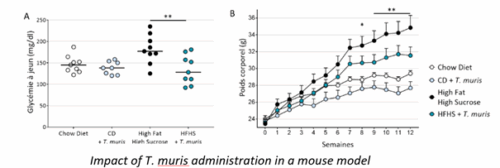
- Proof of concept demonstrated in vivo: In mice fed a high-fat diet, administration of a small amount of the bacteria in parallel yielded the following results:
- After 3 weeks, fasting blood sugar levels in mice that received the bacteria decreased by 40% compared to those that did not receive it;
- After 12 weeks, body mass in mice receiving the bacteria was reduced by 12% compared to those that did not receive it.
IP
- A PCT patent application WO2024/133647, with a priority filing date of 2022/12/22.
- This application has entered the national phase in EU, CA, US, JP, KR, MX.
Valorisation strategy
- Startup
